The growing number of supporters of veganism¹ which is already present in more than 30 million Brazilians, around 14% of the country's population, also indicates an increase in plant foods. This brings to the fore thousands of questions about obtaining nutrients such as protein, which, in short, is widespread from animal sources. And there? Is this replacement really worth it? Today we are going to reveal to you the truth about vegetable proteins so that you can make them a meat substitute in your meals.

What are plant proteins?
First of all, the proteins² are important components of the human diet and play an essential role as structural and functional components of living systems. They provide our body with amino acids (AA) that serve as the building blocks of all vital organs, muscles (including heart muscles), hormones and biological fluids such as blood. And the protein deficiency in the body can impair the integrity of cells that act in damage repair, metabolism, muscle contraction, in addition to destabilizing the transport of oxygen throughout the body.
With increasing environmental awareness, the food industry has been responsible for 26% of human-made greenhouse gas emissions. In view of this, there has been a growing interest in plant-based food, based on foods of plant origin, which offer many benefits for health and the environment. For a long time, it was believed that meat (white or red) was the main source of protein, but we now know that there are many other plant-based protein sources that can be just as nutritious.
One study³ identified that plant-based diets are more environmentally sustainable than diets rich in animal products because they use fewer natural resources and are associated with much less environmental damage. And are the proteins in these foods also of plant origin? Clear!
Do you know the beans that Brazilians love to eat? In addition to being rich in iron, it also has a good amount of protein. Not only him, several foods such as chickpeas, lentils, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, among others, are rich in protein.

What is the difference between plant proteins and animal proteins?
The main difference between vegetable and animal protein is in the composition of the amino acids that constitute them.
While animal-derived proteins are considered complete sources of protein as they contain all the essential amino acids the human body needs, plant-derived proteins may be deficient in some of these amino acids, making them incomplete. However, it is possible to overcome this deficiency through adequate consumption of a variety of plant protein sources, combining different sources to obtain all essential amino acids.
A practical example! Here at Foodz we use the combination of rice and pea protein. Rice is a source of amino acids such as glutamine, aspartic acid, arginine and alanine. Pea is a source of amino acids such as lysine, methionine and cysteine. When combined, the amino acids present in each food complement each other, forming a complete protein.

Other differences can also be found, such as in protein absorption and digestibility, and in environmental and ethical issues related to the consumption of animal foods.
Which font is the best?
There are many plant protein options that can be incorporated into your diet and can vary according to individual nutritional needs. That's why we've prepared a list of 18 vegetable protein options for you to diversify your meals and get the nutrients your body needs. Check it out below! And in the end, find out which is the best source of vegetable protein!
1. Soy bean vegetable protein

Soybeans are a legume rich in plant protein and one of the few plant foods that contain all the essential amino acids. They are a rich source of glutamic acid, aspartic acid and leucine.
2. Vegetable protein from lentils

Lentils are a legume rich in protein and complex carbohydrates. They contain all the essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Lentils are especially rich in lysine.
3. Vegetable protein from beans

4. Quinoa vegetable protein

Quinoa is a pseudocereal rich in proteins and complex carbohydrates. It contains all the essential amino acids, making it a complete source of plant protein. Quinoa is especially rich in lysine and methionine.
5. Almond vegetable protein

Almonds are a type of nut rich in protein, healthy fats, dietary fiber and vitamin E. They contain all the essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Almonds are especially rich in arginine.
6. Pumpkin seed vegetable protein

Pumpkin seeds are a rich source of protein, healthy fats, dietary fiber and minerals such as zinc and magnesium. They contain all the essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Pumpkin seeds are especially rich in arginine and glutamate.
7. Sunflower seed vegetable protein

8. Chia seed vegetable protein

Chia seeds are a rich source of protein, dietary fiber, omega-3 fatty acids and minerals such as calcium and magnesium. They contain all the amino acids.
9. Peanut vegetable protein

Peanuts are a legume rich in protein, healthy fats and dietary fiber. It contains all the essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Peanuts are especially rich in arginine.
10. Spinach vegetable protein

Spinach is a leafy vegetable rich in protein, vitamins and minerals. It contains all the essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Spinach is especially rich in lysine, leucine and tyrosine.
11. Broccoli vegetable protein

Broccoli is a cruciferous vegetable rich in protein, dietary fiber, vitamins and minerals. It contains all the essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Broccoli is especially rich in cysteine, lysine and tryptophan.
12. Vegetable protein from Brussels sprouts

13. Cauliflower vegetable protein

Cauliflower is a cruciferous vegetable rich in protein, dietary fiber, vitamins and minerals. It contains all the essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Cauliflower is especially rich in cysteine and glutamine.
14. Asparagus vegetable protein

Asparagus is a vegetable rich in protein, dietary fiber, vitamins and minerals. They contain all essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Asparagus is especially rich in asparagine and serine.
15. Pea vegetable protein

16. Mushroom vegetable protein

Mushrooms are a type of fungus rich in protein, dietary fiber and minerals such as potassium and phosphorus. They contain all essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Mushrooms are especially rich in glutamine and glutamic acid.
17. Rice vegetable protein

Brown rice is a rich source of protein, complex carbohydrates and dietary fiber. It contains all the essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Brown rice is especially rich in cysteine and methionine.
18. Oat vegetable protein

Oats are a whole grain cereal rich in protein, complex carbohydrates and dietary fiber. It contains all the essential amino acids, although some of them are present in smaller amounts. Oats are especially rich in lysine and tryptophan. Additionally, oats are a good source of beta-glucans, a type of soluble fiber that can help lower cholesterol and improve heart health.
What is the best source of vegetable protein?
In the table below you can see the amount of protein present in each of these sources.
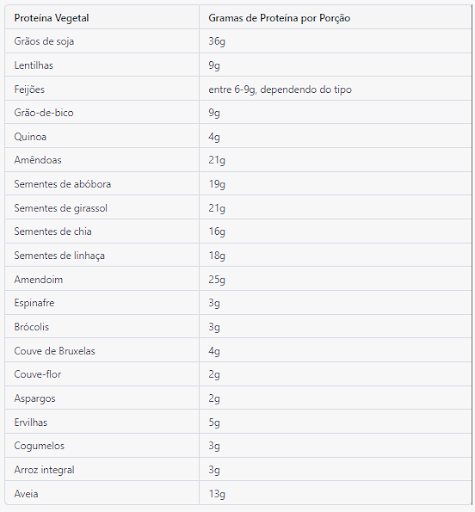
As you might have guessed, based on the analysis of this table, the best source of vegetable protein is soy, because it contains 36g of protein. Remember, you must always look for a combination of 2 or more proteins so that the amino acid value is complete.
At Foodz, we look for the best combination of vegetable protein sources: pea and rice protein. When combined, they provide the body with all the amino acids necessary for a complete and balanced diet. In a single portion of Foodz, we offer 40g of protein. We use high quality proteins, which offer good digestibility and nutrient absorption, in addition to bringing many health benefits. With our combination of plant-based protein sources, you can be sure you're consuming a complete and nutritious meal.

2 PRO Bags + 1 Shaker (26) - R$23.00 per meal
R$ 599
References
- https://veganbusiness.com.br/veganismo-no-brasil-como-funciona/
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition/article/protein-quality-evaluation-twenty-years-after-the-introduction-of-the-protein-digestibility-corrected-amino-acid-score-method/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27886704/